
How secure is a VPN?
A reliable virtual private network (VPN) can be a safe way to browse the internet. VPN security can protect from IP and encrypt internet history and is increasingly used to prevent snooping by government agencies. However, VPNs are not able to keep you safe in all scenarios.
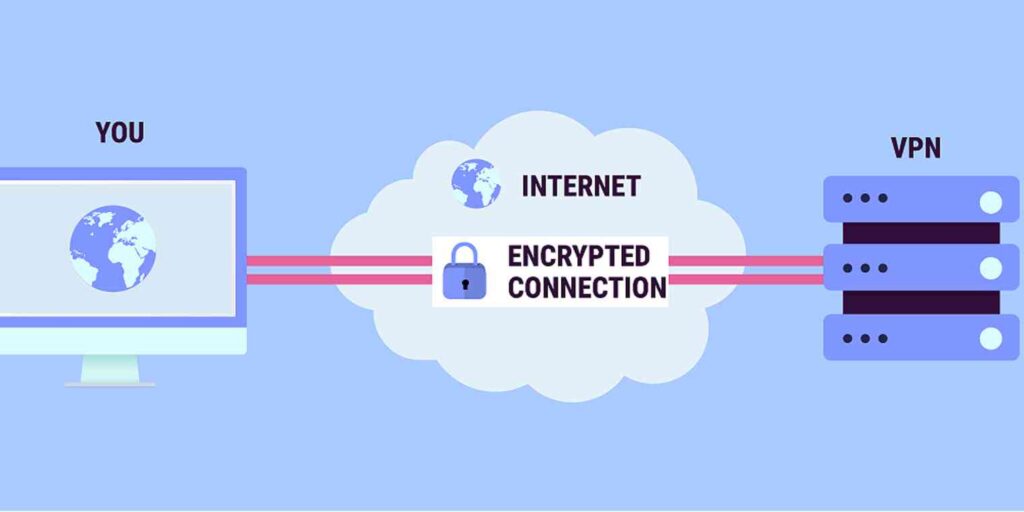
If you are asking what VPN is, it is a virtual network that enables internet users to protect themselves and their organization by creating a private web browsing session. Using a VPN becomes especially important when using public Wi-Fi to prevent others from eavesdropping on your online activity and the data and information they share. A VPN creates a secure tunnel between a user’s computer and the VPN server, which hides their online activity and location.
VPN security enables users to protect their online privacy and prevent their internet service provider (ISP) from tracking their browsing activity. It connects a user’s device to the VPN server, then passes their internet traffic through the VPN provider’s internet connection. This hides browsing information and makes it more difficult for bad actors to gather or monitor the user’s online activity.
Is private browsing private?
You might be asking yourself. “Do I need a VPN when my browser has private browsing?”
Popular web browsers include a private browsing feature, which enables users to browse the web without saving their history, search information, and temporary local data like cookies. Private browsing is available through top browsers, such as Apple Safari on Mac and iOS, Google Chrome’s Incognito mode, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, and Microsoft Edge’s InPrivate Browsing.
A browser’s private browsing mode will prevent data from being stored on a user’s local device or computer. However, it does not necessarily avoid sharing information between the user’s device or computer and their ISP. Furthermore, third parties may be able to detect users’ activity through private browsing sessions, which they can use to exploit their operating system.
Here are a few reasons why Free VPNs are not safe
You should ask yourself, “Is a VPN safe?” and the answer is straightforward.
Using free software is not a practical solution for ensuring VPN security because it often will not protect data and browsing activity on the internet. Key reasons not to use a free VPN include:
- Free VPN tools compromise user security: Many free VPN tools contain malware that cybercriminals could use to steal users’ data, gain unauthorized access to their data or machine, or launch a cyberattack. An ICSI Networking and Security Group research report (link) found that 38% of the 283 Android VPN apps studied contained some form of malware presence. Therefore, a VPN application may not always be safe when using free tools.
- Free VPN tools track online activity: A secure VPN should protect a user’s activity. At the same time, they browse the internet, but some free VPNs do the opposite by tracking users’ online activity. The same ICSI research found that 72% of the free VPN services analyzed embedded third-party tracking tools in their software. This enables VPN tools to collect user information and sell it for a profit to the highest bidders, which allows advertisers to target free VPN users with ads. Some free VPN tools hide information about whether they share or sell user data, but others say so in their privacy policies.
- Free VPN tools limit data usage: VPNs are great for protecting data or hiding a user’s location when watching a movie from a streaming service unavailable in their region. However, a free VPN typically limits the amount of data users can use through the tool. This could include limiting the amount of data they can use per month, limiting the amount of time the VPN is available per browsing session, or unblocking certain websites only. Therefore, free VPN tools are not ideal for people who want to protect their data or mask their location for a considerable time.
- Free VPN tools target users with ads: Free VPNs also use advertising to generate revenue, which means users’ data can be shared or targeted without their permission. This is frustrating for users because ads can also slow down the user’s internet connection or contain malware. The presence of advertisements on a free VPN service can also be a privacy concern because the provider is likely sharing users’ online activity with third-party services. Paid-for VPNs include ad-blocking tools and features like malware protection and unlimited bandwidth, which keep users’ data secure.
- Free VPNs slow down users’ internet speed: Like the data-limiting issue above, free VPNs may provide slower internet speeds than premium tools. Even free VPN options from reputable vendors will give a slower internet connection than available through their paid-for options. They will also prioritize internet speeds for their paying customers, which can further slow down their free services.
Which features make a VPN safe and secure?
The question of how secure VPN services typically depend on the VPN being used. A VPN from a reliable provider will feature encryption for the user’s data and online browsing history to shield them from hackers and ISPs.
Is using a VPN safe? That relies on a provider that ensures online privacy, provides transparent privacy policies, fixes data leaks, and does not track its users. The best VPN tool or application contains the following features:
- Internet Protocol (IP) address leak prevention: The core purpose of a VPN is to hide or disguise a user’s IP address and prevent anyone from tracking their online activity. However, a VPN can sometimes include flaws that result in the user’s IP location being leaked. It is therefore essential to look for a provider that actively prevents IP address leaks. Check reviews online to see if they have a history of IP address leakage.
- No information logging: No-log VPNs do not collect or log data that users share on the network, such as login credentials, files they download, and their search history. This is key to ensuring users’ online privacy and protecting their anonymity from other internet users. It also ensures that a user’s information is protected, even if an attacker gains unauthorized access to a VPN tool. When considering a VPN, check whether it logs online activity, periodically purges data, or discloses user information in any other scenario.
- VPN kill switch: If a VPN connection drops, the user’s internet access will switch to their regular connection. A VPN kill switch feature automatically exits specific programs if an internet connection becomes unstable to reduce the risk of sensitive data being leaked by applications.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Any VPN program should be as secure as possible to ensure that only authorized users can access it. MFA enables users to prove their identity and that they are who they say they are before they are given access to the VPN. For example, upon logging in to the VPN using their username and password, the user can then be sent a code via Short Message Service (SMS) or a notification they can approve on their mobile phone. This extra level of security ensures only the right people can access a VPN and makes it more difficult for hackers to intercept.
If you are using a VPN and want to see if your IP is private, you can use our service. (link)